COVID Injections: Unveiling the Mechanisms of Harm
New pathology, a new wave of disease, and 44 common examples of injection-induced illnesses supported by over 930 scientific publications linking these diseases with the injections.
Introduction
The list of traditional diagnoses arising as sequel from the COVID-19 genetic injections is extensive. Pfizer’s own analysis alone lists over a thousand different diagnosed adverse reactions (Click Here, Page 30-38). The failure and dangers of these genetic experiments were predictable, based on pre-2020 scientific knowledge. Yet, despite diligent efforts to warn the public, elected officials, and bureaucrats, billions of people (many repeatedly) have been subjected to these injections in what can only be described as a radical and unethical medical experiment. In many countries, including Canada, doctors who voiced caution were unlawfully persecuted—our careers, incomes, and reputations tarnished.
Moreover, similar abuses were inflicted upon doctors who reported “vaccine” injuries or attempted to treat patients suffering from COVID-19 “vaccine”-related harm. Consequently, many nurses, doctors, and health professionals who remain within the system have become victims of this unlawful injection campaign themselves. In many cases, they either cannot or will not recognize the emergence of a new cause behind the dramatic rise in deaths and diagnoses, ranging from infections and cancers to blood clots, myocarditis, miscarriages, infertility, and much more.
The New Wave of Disease
This blind spot in healthcare is causing yet another wave of harm. Individuals injured by these injections are being diagnosed using outdated criteria, and are receiving treatments that do not address the true underlying cause—the COVID injections themselves. If we are to offer hope and optimize outcomes for the billions affected, we must rectify this critical flaw in modern healthcare.
The purpose of this article is to illuminate some of the key mechanisms by which these injections are causing disease and death. Understanding the pathophysiology behind these conditions is critical for advancing life-saving care. Note that the new pathology of these injection-induced illnesses is different from prior medical understanding. Although the symptoms are similar, traditional treatments may be extremely limited without addressing the root of the issue.
Mechanisms of Harm
C-19 Modified mRNA Injections Contents
The injections contain a variety of components, including their declared ingredients, which are modified mRNA within pegylated lipid nanoparticles (pegLNPs). PegLNPs are tiny nanoparticles with nearly limitless tissue penetration. They deliver their genetic payloads into all tissues, including the brains, ovaries, testicles, and unborn children of any pregnant women injected.
The mRNA is modified by substituting N1-methylpseudouridine in place of uridine. This gives the RNA an unusually long lifespan of at least half a year, compared to natural mRNA, which typically lasts only a few hours. As a result, the subjects' cells continue producing the foreign coronavirus spike protein for an extended period.
This modification involving N1-methylpseudouridine also introduces errors in reading the RNA, leading to the production of a wide array of unpredictable and random proteins in addition to the spike proteins. The production of these toxic spike proteins and other protein products continues for at least six months and possibly much longer.
The injections also contain various undeclared contents and contaminants, including chemical contaminants and an array of plasmid DNA. The plasmid DNA includes a list of concerning genetic sequences, which are still under investigation. These include the presence of SV40 enhancer and SV40 promoter sequences—genetic engineering tools used to facilitate the incorporation of foreign DNA into the subjects' chromosomes. This raises the serious risk of permanent genetic modification in the human subjects. Research on this issue is ongoing, though we already have laboratory cell culture evidence of genetic integration of this DNA into human chromosomes.
Nanoparticle toxicity & Polyethylene Glycol
Lipid nanoparticles have known serious toxic effects, especially if injected repeatedly, which the C-19 injections are. Polyethylene glycol triggers adverse immune responses in many people.


Toxic Spike Proteins
Coronavirus spike proteins (SP) are known toxins. The spike protein of the engineered SARS-CoV-2 virus—whether from the virus itself or produced in subjects' cells following the injections—exhibits enhanced toxicity compared to natural coronavirus spike proteins. These modifications include the incorporation of a furin cleavage site and the elimination of hemagglutinin esterase expression on the surface of the spike protein.
Blood clotting
The elimination of hemagglutinin esterase contributes to the spike protein's exceptional ability to cause blood clots at both the microscopic and macroscopic levels.
Blood Vessel Erosion
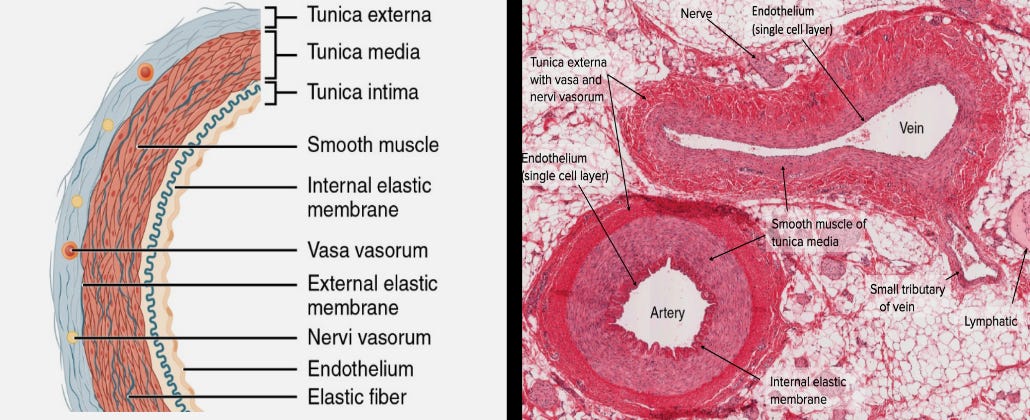
The innermost layer of cells lining blood vessels is exposed to circulating pegylated nanoparticles from the injections. These particles deliver the spike protein genetic code into the cells, causing them to produce SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins and express them on their surface. This marks these cells as foreign, triggering an immune system attack. The inner layer of cells is destroyed and sloughs off, exposing the underlying cells to the same process. In this way, the tunica intima—the innermost layer of blood vessel walls—and even deeper tissue layers of arteries and veins are damaged, eroded, and weakened. This exacerbates the enhanced blood-clotting effects of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, as damaged blood vessel walls are potent triggers for clot formation.
Accelerated deterioration and aging of many organs
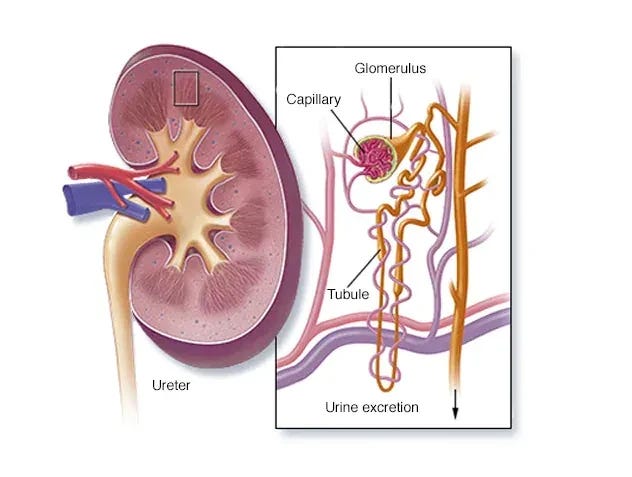
Ongoing microvascular clotting is a contributing mechanism that accelerates organ deterioration, causing the organs of victims to age faster than normal. This can lead to a variety of clinical conditions, including accelerated microvascular dementia and kidney failure.
Reverse ORF, Spider Silk Protein, and “Calamari Clots”
One of the unusual findings in the genetic analysis of the undeclared plasmid DNA content of the C-19 mod-mRNA injections is a reverse open reading frame at the end of the plasmid DNA sequence coding for the spike protein. This causes ribosomes to also read the spike protein genetic sequence in the reverse direction, resulting in a completely different protein. The reverse sequence contains significant sections resembling the highly unusual proteins found in spider silk. This may help explain the unusual white, rubbery proteinaceous 'clots' extracted from the arteries and veins of many deceased injection victims by morticians and pathologists. The nature of these clots and the reverse translation of the spike protein genetic sequence require further study.
Quasi-autoimmune pathology
Cells that produce the spike protein, as well as cells to which the spike protein adheres via ACE2 receptors, display a foreign protein on their surface. This triggers the subjects’ immune systems to attack these spike-protein-laden cells and tissues as if they were foreign, or 'non-self.' This is one of the major mechanisms of injury observed in the first year following the injections. Autopsy samples from young hearts, testicles, ovaries, kidneys, brains, placentas, and other tissues show affected organs heavily laced with spike protein and under intense autoimmune attack by the subjects' own immune systems. This resembles organ rejection seen in transplants, where the victims’ organs appear foreign to their immune system and are 'rejected.'
‘Spiked’ tissues undergoing this autoimmune attack may lead to clinical presentations in the days or months following injection, but can also contribute to progressive damage and the accelerated aging of many organs and tissues.
Antigenic Mimicry and Autoimmune Diseases
The spike protein also bears some resemblance to numerous natural proteins in the body, including syncytin-1, an essential protein in both female and male reproductive tissues. The immune response triggered against the spike protein can also target these natural proteins, causing another collection of autoimmune diseases and adverse effects, including miscarriages and infertility.
Ribosome Frame Shifting and More Autoimmune Disease
Due to the modified uridine in the injected mRNA, ribosome frame shifting occurs, which means that many errors are made as our cells' ribosomes read the mRNA. In addition to predominantly producing the spike protein, a large array of random proteins and protein fragments are generated. Each of these has the potential to resemble a natural protein in the body sufficiently to trigger more autoimmune diseases.
Antibody Dependent Enhancement (ADE)
The production of large amounts of spike protein within the subjects' bodies triggers a dramatic production of adaptive antibodies to the spike protein. These antibodies have various toxic effects, including the enhancement of coronavirus infections. This is one of the reasons that we observe increased rates of COVID infection, hospitalization, and death among the “vaccinated” versus the “unvaccinated.” This process is called antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE). Experimental vaccination against coronaviruses, especially against their spike protein, has been associated with a high incidence of ADE. In these experiments, like the current global experiment on humans, the antibodies produced by vaccination end up helping the virus infect the subjects rather than providing protection.
Immune System Damage, Increased Cancer and All Infections
The subjects' dramatic immune response to the spike protein produced following the injections weakens the immune system in various ways, including the suppression of CD4 and CD8 positive T cells. This damage to the subjects' immune systems is one factor accounting for the rise in cancers, particularly aggressive cancers, and a wide variety of infections among the “vaccinated.
Multiple Mechanisms to Cause Cancer
The injections have multiple mechanisms for causing cancer. These include immune system damage and chromosomal DNA damage. The insertion of foreign genetic material into the human genome has many harmful effects that are still being discovered, including the disruption of various tumor suppression genes that normally protect our DNA from damage and defend us against cancer.
Additionally, the spike protein (SP) of SARS-CoV-2 and these injections has many unique characteristics, including the capacity to migrate into our cells’ nuclei and damage the DNA, thereby interrupting tumor suppressor genes. This adds further potential mechanisms for causing cancer.
Antibody Mediated Selection: Driving the Evolution of Variants and Extending the Pandemic
Another reason many of us warned against this genetic “vaccine” program is the issue of Antibody Mediated Selection (AMS). AMS explains that although vaccination may play a role in averting a pandemic before it occurs, it is likely to prolong a pandemic and drive the evolution of one variant after another if administered during an ongoing pandemic. This serves as the foundation for a golden rule of vaccinology: we should never try to vaccinate our way out of a pandemic. Attempting to do so drives the evolution of the virus, creating one variant after another. These variants are particularly dangerous to the “vaccinated” subjects, as opposed to those with natural exposure and immunity. Natural immunity is broad and responds to many aspects of the virus, so the virus cannot simply adapt its spike protein to evade it. However, due to the injection campaigns, we have extended what would naturally have been a few months of active infections to now four years of variants, infections, and more misguided injections. This has been profitable for the vaccine industry but devastating for mankind.
Dr Geert Vanden Bossche explains: The Great Mistake (Pt1)
Dr Geert Vanden Bossche PhD is a world renowned expert in immunology & vaccinology. He has been courageous and self-sacrificing in warning and educating the world regarding covid-19 and the grave error of vaccinating during a pandemic, especially that of a coronavirus.
Additional Mechanisms of Injury
There are additional mechanisms of injury, including prion diseases, and more research is needed regarding the injury mechanisms associated with these injections. The details of the immune system disturbances caused by these injections are extensive. This presentation serves as just a brief introduction.
Here is Pfizer's 393 page record of 4,964,106 adverse events that were reported up until June 18, 2022.
Where do we go from here?
COVID-19 genetic 'vaccines' offer no benefit and cause significant harm. It is long overdue to halt their manufacturing and administration. We must reinstate the scientists and doctors who have been warning about these issues, while advancing research and treatment of the resulting injuries, despite having been stripped of our positions, laboratories, and incomes. Understanding the mechanisms of injury and how to treat them, and urgently distributing this information, should be our highest priority.
New pathophysiologic mechanisms are driving dramatic increases in disease, disability, and death worldwide. The medical and scientific communities have been muzzled and co-opted, leaving healthcare practitioners 'flying blind.'
It is time to end the suppression and manipulation of medical science. We must urgently advance our understanding and treatment of the toxic effects of the COVID-19 genetic 'vaccines.'
44 examples of COVID 'vaccine'-induced diseases, backed by 930 scientific articles linking these conditions to the injections
The injection-induced illnesses listed here are defined according to their classifications prior to the introduction of the COVID-19 injections. While these emerging illnesses share common symptoms with conventional conditions, their underlying pathology is different. The mechanisms of injury described above must be considered, as existing medical treatments will fail to address the new root cause of these diseases.
Thanks to the community at CovidVaccineInjuries.com for compiling the studies that became the foundation of this resource. See the footnotes for the complete list of the aforementioned 930+ scientific articles. Please share this resource with patients, healthcare providers, and lawyers.
Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and is not intended to be medical advice.
Table of Contents
There are many more adverse event diagnosis linked to the Covid-19 genetic “Vaccines”. We will continue to expand this reference article. Meanwhile here is Pfizer's 393 page record of 4,964,106 adverse events that were reported up until June 18, 2022: Click Here
Acute Hyperactive Encephalopathy
Acute Hyperactive Encephalopathy refers to a sudden and intense alteration in brain function characterized by increased activity. It often manifests with symptoms such as confusion, agitation, hyperactivity, and altered consciousness. Various factors, including infections, metabolic disturbances, or drug reactions, can trigger this condition.
Acute Hyperactive Encephalopathy references1
Acute Kidney Injury
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) is a sudden and rapid decline in kidney function, leading to a build-up of waste products in the blood. Common causes include dehydration, infections, or medication reactions. Symptoms may include decreased urine output, swelling, and confusion.
Acute Kidney Injury references2
Acute (Transverse) Myelitis
Acute (Transverse) myelitis is a rare neurological disorder characterized by the sudden inflammation of the spinal cord, leading to motor and sensory deficits. It can result from various causes, including viral infections, autoimmune disorders, or other inflammatory conditions. Symptoms include pain, weakness, numbness, and difficulty with bladder and bowel control. Diagnosis involves clinical evaluation, imaging studies like MRI, and cerebrospinal fluid analysis.
Acute (Transverse) Myelitis references3
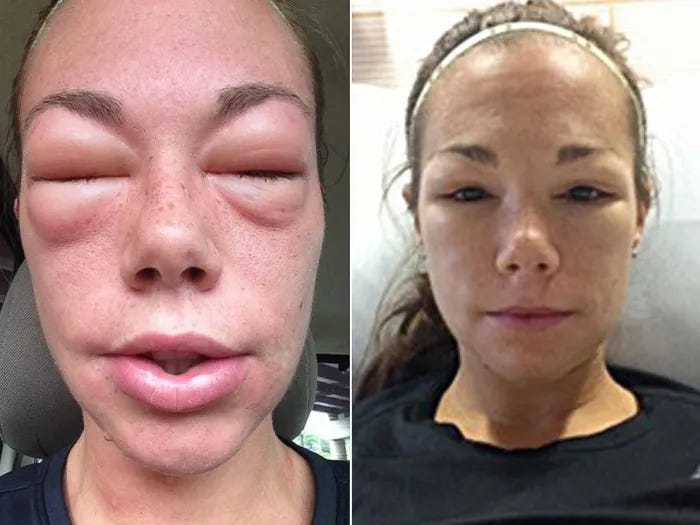
Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions occur when the immune system overreacts to substances (allergens) like foods, medications, or insect stings. Upon exposure, the immune system releases chemicals, such as histamine, causing symptoms like hives, itching, swelling, and in severe cases, anaphylaxis. Common allergens include nuts, pollen, and certain medications. Reactions can range from mild to life-threatening, requiring immediate medical attention. Diagnosis involves evaluating symptoms and sometimes using allergy testing.
Allergic Reactions references4
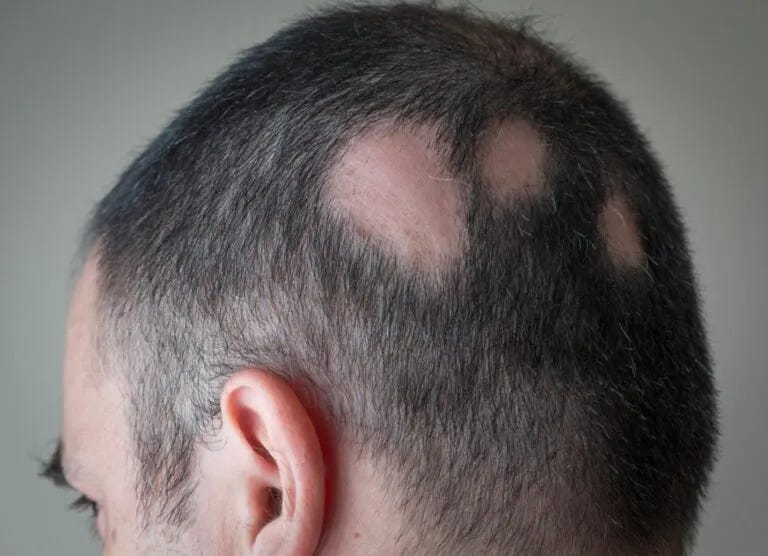
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss in localized patches. The immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to hair loss. It can affect any hair-bearing area, including the scalp, eyebrows, and beard. The exact cause is unclear, but genetics and environmental factors may contribute. While the hair follicles are not permanently damaged, treatments like corticosteroids can help stimulate hair regrowth. The condition's course is unpredictable, with spontaneous regrowth or recurrent episodes possible.
Alopecia Areata references5
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a severe and potentially life-threatening allergic reaction that occurs rapidly after exposure to an allergen. It involves a systemic release of chemicals, such as histamine, triggering widespread inflammation. Common allergens include certain foods, insect stings, medications, and latex. Symptoms can escalate quickly, affecting multiple organ systems and leading to difficulty breathing, a drop in blood pressure, hives, and swelling, particularly in the face and throat. Anaphylaxis requires immediate medical attention, as it can progress rapidly and lead to respiratory failure or cardiovascular collapse.
Anaphylaxis references6
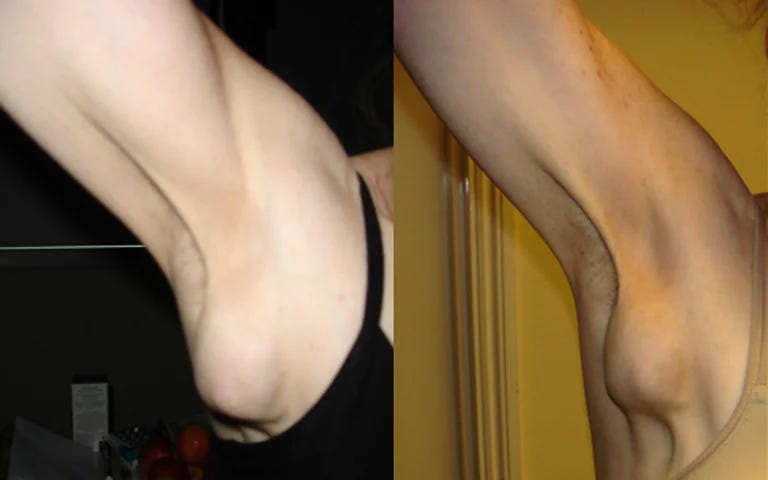
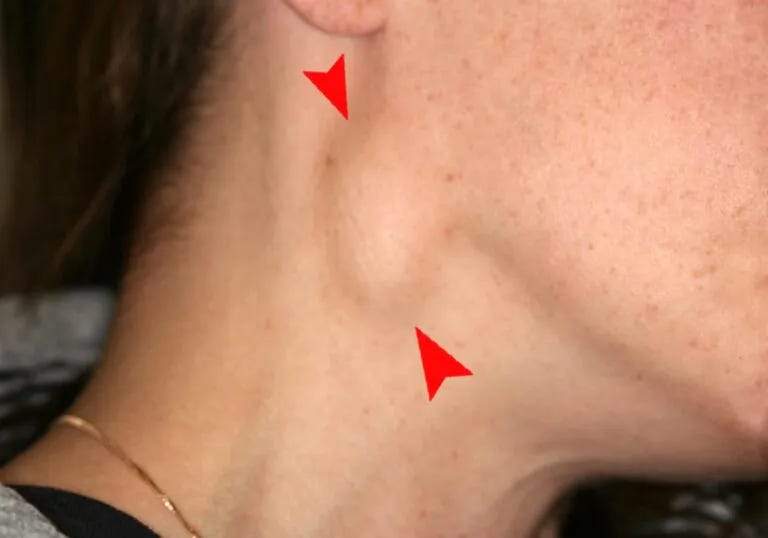
Axillary Adenopathy
Axillary adenopathy refers to the enlargement or swelling of lymph nodes in the armpit (axilla). Lymph nodes are part of the immune system and can become enlarged in response to various conditions. Common causes of axillary adenopathy include infections, such as localized skin infections or systemic illnesses, as well as inflammatory or neoplastic disorders. The swelling may be tender or painless and can be associated with other symptoms like fever or fatigue, depending on the underlying cause. Diagnosis involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and sometimes imaging or biopsy.
Axillary Adenopathy references7
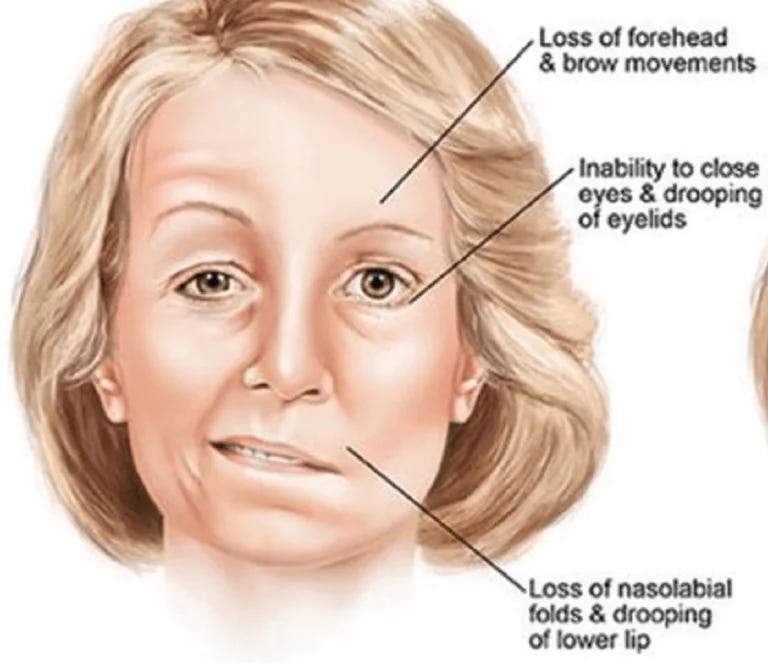
Bell’s Palsy
Bell's Palsy is a sudden, temporary weakness or paralysis of the facial muscles, typically affecting one side of the face. The exact cause is often unclear, but it's thought to involve inflammation of the facial nerve, which controls facial muscles. Viral infections, particularly the herpes simplex virus, are frequently implicated. Symptoms include drooping of the mouth, difficulty closing the eye on the affected side, altered sense of taste, and facial twitching.
Bell’s Palsy references8
Bullous Drug Eruption
Bullous drug eruption is a severe skin reaction marked by the development of large, fluid-filled blisters (bullae) on the skin. It is an uncommon side effect of certain medications, leading to widespread blistering and skin detachment. Lyell's syndrome, or toxic epidermal necrolysis, is an extreme form of bullous drug eruption characterized by extensive skin detachment, often requiring urgent medical intervention due to the risk of complications and mortality.
Bullous Drug Eruption references9
Capillary Leak Syndrome
Capillary Leak Syndrome (CLS) is a rare disorder characterized by sudden and severe leakage of fluids from blood vessels into surrounding tissues. This can lead to a rapid drop in blood volume, causing symptoms like swelling, low blood pressure, and organ dysfunction. CLS may be triggered by various factors, including infections or certain medications.
Capillary Leak Syndrome references10
Cardiac Complications
Cardiac complications refer to adverse effects impacting the heart, often resulting from conditions like heart disease, infections, or other medical issues. These may manifest as irregular heart rhythms, heart failure, or damage to the heart muscle.
Cardiac Complications references11
Central Serous Retinopathy
Central Serous Retinopathy (CSR) is an eye disorder characterized by fluid accumulation beneath the retina, causing central vision distortion. This condition often affects men, primarily those in their 30s to 50s. Potential triggers include stress, corticosteroid use, and hypertension. Symptoms may include blurred or distorted vision. Although CSR often resolves on its own, persistent cases may require medical intervention, such as laser therapy.
Central Serous Retinopathy references12
Cerebral Venous Thrombosis
Cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT) is a rare but serious condition characterized by the formation of blood clots in the cerebral veins or sinuses, impeding blood drainage from the brain. This can lead to increased pressure within the brain, potentially causing severe headaches, visual disturbances, seizures, and neurological deficits. Risk factors include genetic predisposition, hormonal changes (such as those during pregnancy or contraceptive use), infections, and certain medical conditions. Diagnosis often involves imaging studies like MRI or CT scans.
Cerebral Venous Thrombosis references13
Cutaneous Adverse Effects
Cutaneous adverse effects refer to skin reactions resulting from exposure to external factors, often drugs or vaccines. Lyell's syndrome, or toxic epidermal necrolysis, exemplifies a severe cutaneous adverse reaction. It is a rare, life-threatening condition characterized by widespread skin detachment and mucous membrane involvement. Such reactions can manifest as rashes, hives, or more severe conditions like Lyell's syndrome, highlighting the importance of monitoring and promptly addressing skin-related adverse events in medical contexts.
Cutaneous Adverse Effects references14
Facial Nerve Palsy
Facial nerve palsy is a condition characterized by weakness or paralysis of the muscles on one side of the face, often resulting in drooping, impaired facial expressions, and difficulty closing the eye. Causes include viral infections, trauma, or tumors affecting the facial nerve. Symptoms may range from mild to severe.
Facial Nerve Palsy references15
Guillain-Barré Syndrome
A neurological disorder in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks part of its peripheral nervous system—the network of nerves located outside of the brain and spinal cord. Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) can range from a very mild case with brief weakness to nearly devastating paralysis, leaving the person unable to breathe independently. Fortunately, most people eventually recover from even the most severe cases of GBS. After recovery, some people will continue to have some degree of weakness.
Guillain-Barré Syndrome References16
Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
An aggressive and life-threatening syndrome of excessive immune activation. It most frequently affects infants from birth to 18 months of age, but the disease is also observed in children and adults of all ages.
Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis references17
Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
Henoch-Schonlein Purpura (HSP) is a rare autoimmune disorder primarily affecting children. It involves inflammation of small blood vessels, leading to purplish skin rash, joint pain, abdominal pain, and kidney inflammation. The exact cause is unknown, but it often follows respiratory infections. Most cases resolve on their own, but severe complications can occur.
Henoch-Schonlein Purpura references18
Immune-Mediated Disease Outbreaks
Immune-mediated disease outbreaks involve the rapid spread of illnesses triggered by the immune system's abnormal response to the body's tissues. This can result in various conditions, from autoimmune disorders to hypersensitivity reactions. These outbreaks may stem from infections, genetic factors, or environmental triggers. Examples include rheumatoid arthritis and allergic reactions.
Immune-Mediated Disease Outbreaks references19
Immune-Mediated Hepatitis
Immune-mediated hepatitis is a condition where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the liver cells, leading to inflammation and liver dysfunction. It can result from various triggers, including infections, drugs, or autoimmune processes. Symptoms may include fatigue, jaundice, abdominal pain, and elevated liver enzymes. Diagnosis involves blood tests and imaging studies.
Immune-Mediated Hepatitis references20
Internal Bleeding
Internal bleeding refers to the escape of blood from blood vessels inside the body. It can occur due to trauma, underlying medical conditions, or spontaneously. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, and signs of shock. Prompt medical attention is crucial to prevent complications.
Internal Bleeding references21
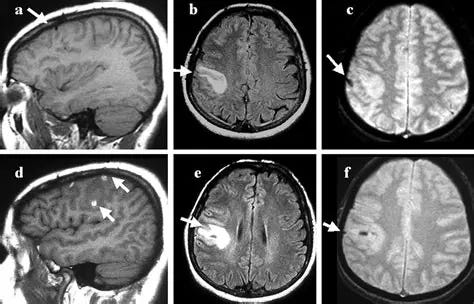
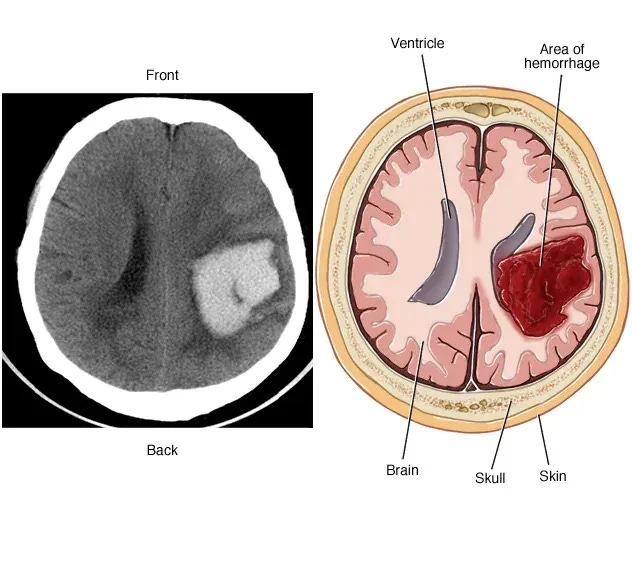
Intracerebral Haemorrhage
Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) is a type of stroke characterized by bleeding within the brain tissue, typically caused by the rupture of a blood vessel. This bleeding leads to the accumulation of blood and increased pressure, potentially causing neurological damage. Symptoms may include sudden and severe headaches, focal neurological deficits, and altered consciousness. Common risk factors include hypertension, cerebral amyloid angiopathy, and certain blood-thinning medications. Diagnosis involves imaging studies such as CT scans.
Intracerebral Haemorrhage references22
Lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy refers to the abnormal enlargement of lymph nodes, which are small, bean-shaped structures that play a crucial role in the immune system. This condition can be a symptom of an underlying infection, inflammation, or, in some cases, malignancy. Lymph nodes may swell as they respond to infections, such as viral or bacterial, or due to inflammatory conditions like autoimmune diseases. Common locations for lymphadenopathy include the neck, armpits, and groin. The enlargement is often accompanied by tenderness and may be associated with other symptoms like fever and fatigue. Diagnosis involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and sometimes imaging or biopsy.
Lymphadenopathy references23
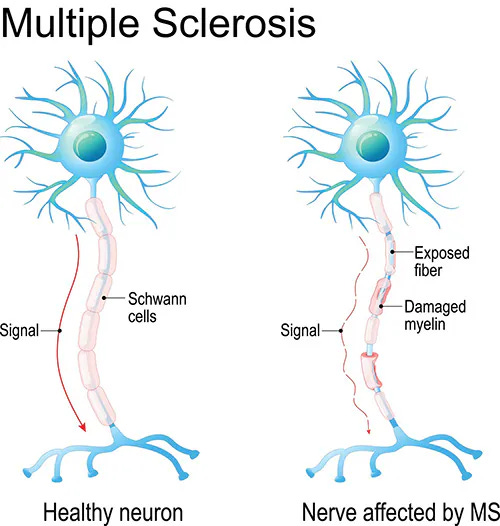
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease affecting the central nervous system, causing inflammation and damage to the protective covering of nerve fibers. This disrupts communication between the brain and the body, leading to various symptoms such as fatigue, numbness, weakness, and difficulty with coordination and balance. The course of MS is unpredictable, with periods of relapse and remission.
Multiple Sclerosis references24
Myocarditis
Myocarditis is an inflammatory condition affecting the myocardium, the middle layer of the heart wall. It is typically caused by viral infections, although bacteria, parasites, and certain medications can also contribute. The inflammation can weaken the heart muscle, impairing its ability to pump blood efficiently. Symptoms may include chest pain, fatigue, shortness of breath, and an irregular heartbeat. Severe cases can lead to heart failure or sudden cardiac arrest. Diagnosis involves medical history, physical exams, and imaging tests such as MRI or biopsy.
Myocarditis references25
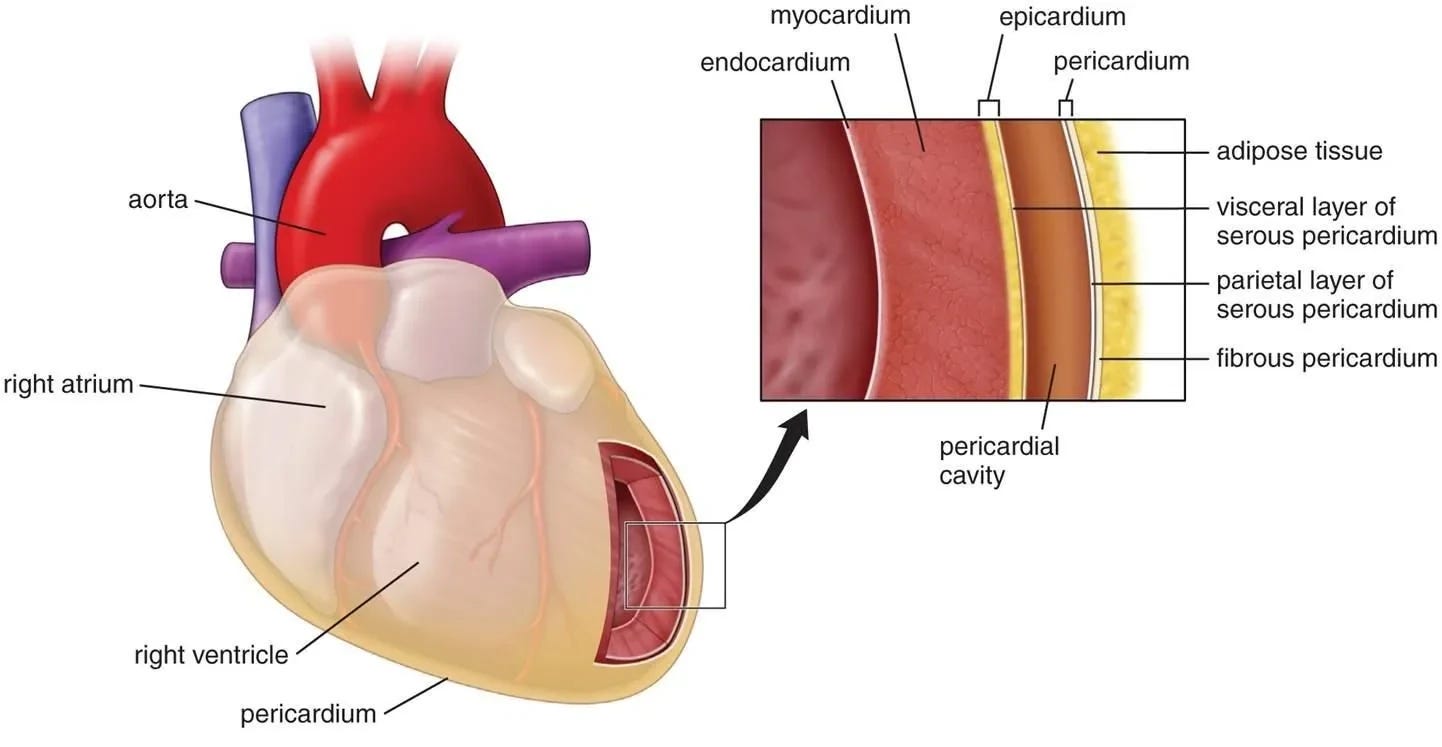
Myopericarditis
Myopericarditis is a condition characterized by inflammation involving both the heart muscle (myocardium) and the pericardium (the protective sac around the heart). It often results from viral infections, although bacterial or autoimmune causes can contribute. The inflammation weakens the heart muscle and may lead to chest pain, fatigue, and symptoms similar to myocarditis. Additionally, pericardial involvement can cause chest discomfort and may lead to complications like pericardial effusion. Diagnosis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, imaging studies (such as MRI or echocardiogram), and sometimes a biopsy.
Myopericarditis references26
Nephrotic Syndrome
Nephrotic syndrome is a kidney disorder characterized by increased protein leakage into urine, leading to swelling, low protein levels, and high cholesterol in the blood. It results from damage to the kidney's filtering units (glomeruli). Symptoms include edema, fatigue, and foamy urine.
Nephrotic Syndrome references27
Neurological Symptoms
Neurological complications refer to adverse effects affecting the nervous system. These may result from various conditions, such as infections, injuries, autoimmune disorders, or metabolic abnormalities. Symptoms include altered sensation, muscle weakness, cognitive impairment, and more.
Neurological Symptoms references28
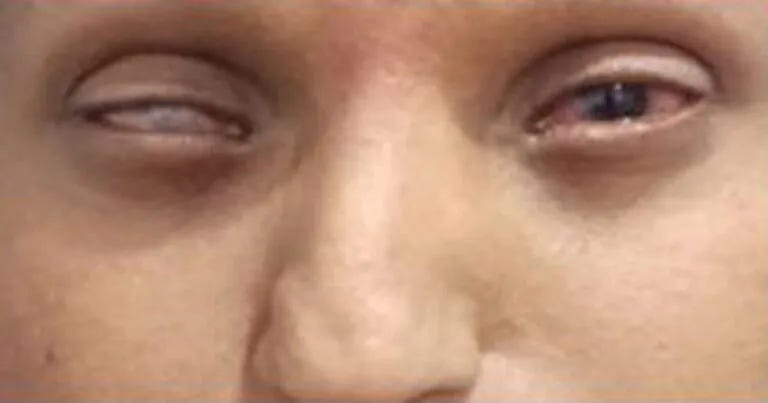
Oculomotor Paralysis
Oculomotor paralysis refers to the dysfunction of the oculomotor nerve, affecting eye movement control. This condition can lead to impaired coordination, double vision, and difficulty focusing.
Oculomotor Paralysis references29
Pericarditis
Pericarditis is inflammation of the pericardium, the sac around the heart. It causes chest pain, often sharp and worsened by breathing. Myopericarditis involves inflammation of both the pericardium and the heart muscle (myocardium), while myocarditis solely targets the myocardium. Pericarditis and myopericarditis typically result from infections or autoimmune disorders, while myocarditis often stems from viral infections. The key difference lies in the extent of inflammation, with pericarditis affecting the pericardium and myopericarditis involving both the pericardium and myocardium. Symptoms overlap, but myopericarditis might present with additional cardiac manifestations. Diagnosis involves imaging and blood tests.
Pericarditis references30
Perimyocarditis
Perimyocarditis refers to inflammation involving both the outer layer of the heart (pericardium) and the adjacent heart muscle (myocardium). It shares characteristics with pericarditis and myocarditis. Commonly caused by viral infections or autoimmune processes, perimyocarditis manifests as chest pain, fatigue, and potential cardiac complications. Diagnosis involves clinical assessment, imaging (such as MRI), and laboratory tests.
Perimyocarditis references31
Petechiae
Petechiae are small, red or purple spots on the skin caused by bleeding under the skin. Resulting from broken capillaries, they appear as pinpoint-sized dots and may signal various medical conditions like platelet disorders, infections, or trauma. Petechiae can also be associated with severe conditions like meningitis or certain bleeding disorders.
Petechiae references32
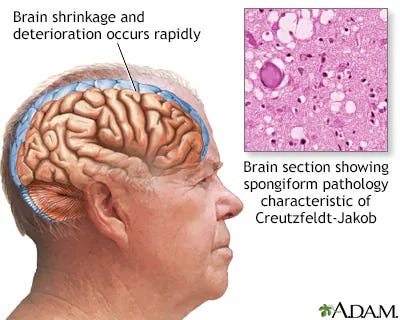
Prion Disease
Prion diseases are a group of rare and fatal neurodegenerative disorders caused by abnormal proteins called prions. These misfolded proteins accumulate in the brain, leading to neuronal damage. Prion diseases, such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, result in rapidly progressive cognitive and motor dysfunction. The abnormal prions induce the misfolding of normal proteins, creating a self-perpetuating cycle of protein aggregation and neurotoxicity.
Prion Disease references33
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin disorder characterized by red, inflamed patches with silvery scales. The immune system mistakenly accelerates skin cell turnover, causing excessive cell buildup on the surface. This results in the formation of raised, scaly plaques.
Psoriasis references34
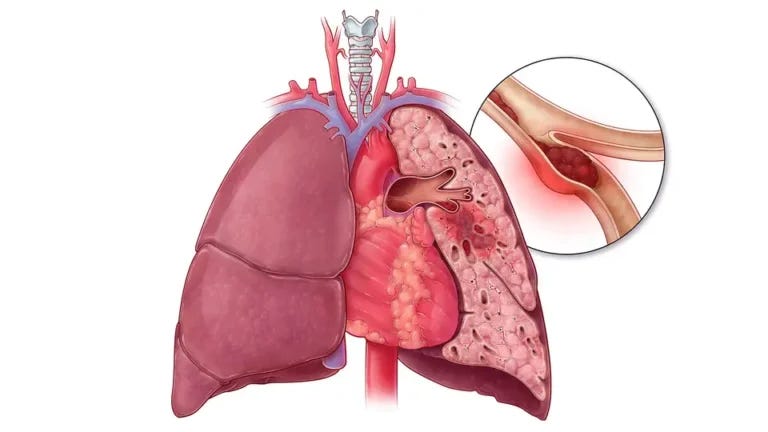
Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a serious medical condition where a blood clot, typically originating in the legs, travels to the lungs and blocks a pulmonary artery. This obstruction can lead to restricted blood flow, causing symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, and cough. Risk factors include deep vein thrombosis, surgery, prolonged immobility, and certain medical conditions. Prompt diagnosis through imaging, such as CT pulmonary angiography, is crucial.
Pulmonary Embolism references35
Purpura Annularis Telangiectodes
Purpura annularis telangiectodes (PAT) is a rare skin disorder characterized by reddish-purple, ring-shaped skin lesions with central clearing and dilated blood vessels (telangiectasia). It falls under the category of pigmented purpuric dermatoses.
Purpura Annularis Telangiectodes references36
Rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis is a serious condition characterized by the breakdown of muscle tissue, releasing a protein called myoglobin into the bloodstream. This can lead to kidney damage and other complications. Causes include trauma, muscle injury, medications, or metabolic disorders. Symptoms may include muscle pain, weakness, and dark urine. Diagnosis involves blood tests and urine analysis.
Rhabdomyolysis references37

Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues throughout the body. Symptoms vary widely, ranging from joint pain and skin rashes to more severe complications affecting organs like the kidneys and heart.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus references38
Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy, often called "broken heart syndrome," is a temporary heart condition characterized by sudden and intense chest pain, shortness of breath, and changes in heart function. It can be triggered by severe emotional or physical stress, leading to a unique ballooning of the heart's left ventricle. Despite its initial severity, Takotsubo cardiomyopathy is typically reversible, and the heart often returns to normal function.
Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy references39
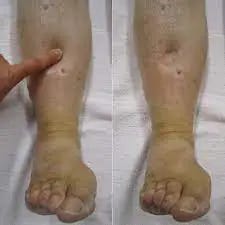
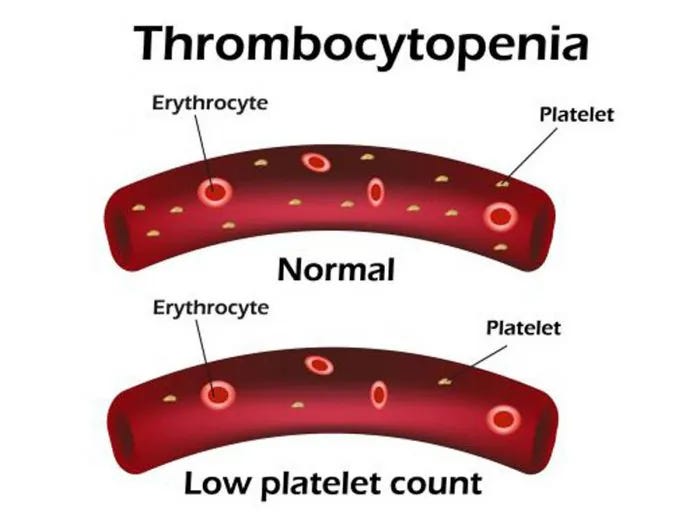
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia is a medical condition characterized by a low platelet count in the blood. Platelets are crucial for blood clotting, and a decreased count can lead to increased bleeding and difficulty forming clots. Various factors contribute to thrombocytopenia, including immune system disorders, medications, infections, or bone marrow disorders. Symptoms may include easy bruising, petechiae (small red or purple spots on the skin), and prolonged bleeding from minor injuries. Diagnosis involves blood tests to measure platelet levels and assess their functionality.
Thrombocytopenia references40
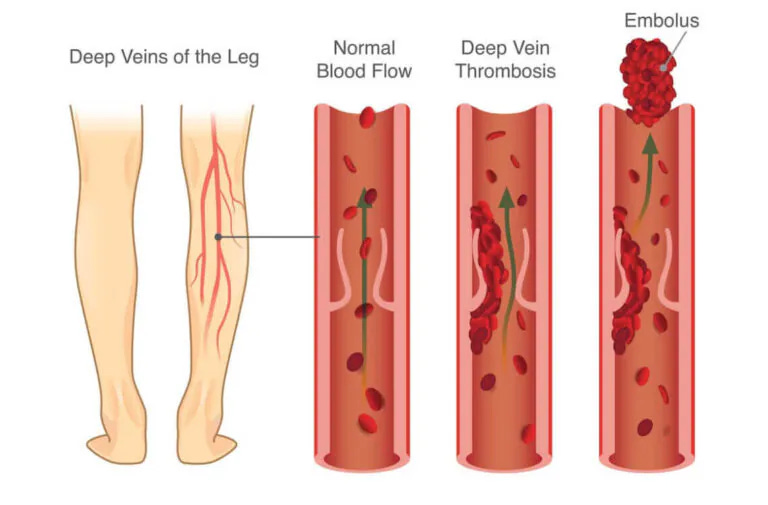
Thrombosis
Thrombosis is a medical condition characterized by the formation of blood clots within blood vessels, obstructing normal blood flow. These clots, known as thrombi, can develop in arteries or veins, leading to serious complications. Arterial thrombosis may result in conditions such as stroke or heart attack, while venous thrombosis can cause deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism. Various factors contribute to thrombosis, including immobility, surgery, genetic predisposition, or underlying medical conditions. Symptoms depend on the location and extent of the clot but may include pain, swelling, and redness. Diagnosis involves imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scans.
Thrombosis references41
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) is a rare blood disorder characterized by widespread clot formation in small blood vessels, leading to low platelet count and potential organ damage. Often caused by a deficiency in ADAMTS13 enzyme, vital for preventing excessive clotting, TTP results in microvascular thrombosis. Symptoms include purpura, neurological issues, fever, and kidney dysfunction.
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura references42
Vasculitis
Vasculitis is a group of inflammatory disorders characterized by the inflammation of blood vessels. The immune system mistakenly attacks blood vessel walls, leading to swelling, narrowing, and possible blockages. Vasculitis can affect arteries, veins, and capillaries throughout the body, impacting various organs and tissues. The exact cause is often unknown, but it may result from infections, autoimmune diseases, or certain medications. Symptoms vary based on the affected vessels and organs but may include fatigue, fever, weight loss, and organ-specific issues. Diagnosis involves clinical evaluation, blood tests, imaging studies, and sometimes a biopsy.
Vasculitis references43
Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada Syndrome
Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada (VKH) Syndrome is a rare autoimmune disorder affecting melanin-containing tissues, particularly the eyes, ears, skin, and meninges. Characterized by inflammation, it often results in bilateral uveitis, hearing loss, and skin depigmentation. The immune response targets melanocytes, leading to a spectrum of symptoms.
Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada Syndrome references44
Closing Statement
We hope you find this comprehensive resource useful in your applied understanding of diseases potentially caused by the COVID-19 mRNA genetic therapy injections. If you would like to support this work, please subscribe to my Substack and share my material.
References
Mechanism of Harm
BNT162b2 - 5.3.6 Cumulative Analysis of Post-authorization Adverse Event Reports
Effectiveness of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Bivalent Vaccine
Furin Cleavage Site in the SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Glycoprotein
Hypersensitivity to Polyethylene Glycol in Adults and Children: An Emerging Challenge
SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Impairs Endothelial Function via Downregulation of ACE 2
COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines Contain Excessive Quantities of Bacterial DNA: Evidence and Implications
Jessica Rose, Substack - What a Tangled Web We May Have Weaved
Striking Similarity Between Human Syncytins and the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein
N1-Methylpseudouridylation of mRNA Causes +1 Ribosomal Frameshifting
Why So Many Vaccinated People Are Getting Sick: Antibody Dependent Enhancement (ADE)
How COVID Jabs Harm the Immune System & Help New Variants Evolve
Global Cancer Rates Exploding Post Vaccines & Being Covered Up
SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein in the Pathogenesis of Prion-like Diseases
Pfizer’s own documents: Cumulative and Interval Summary Tabulation of Serious and Non-Serious Adverse Reactions from Post-Marketing Data Sources (21 June, 2022)
Acute Hyperactive Encephalopathy references
Acute Kidney Injury references
Acute (Transverse) Myelitis references
Acute Myelitis and ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccine: Coincidental or Causal Association
Extensive Longitudinal Transverse Myelitis After ChAdOx1 nCOV-19 Vaccine: Case Report
Acute Transverse Myelitis After SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination: Case Report and Review of the Literature
Acute Transverse Myelitis Following Inactivated COVID-19 Vaccine
A Case of Longitudinally Extensive Transverse Myelitis Following Covid-19 Vaccination
Post COVID-19 Transverse Myelitis; A Case Report with Review of the Literature
Extensive Longitudinal Transverse Myelitis Following AstraZeneca COVID-19 Vaccination
Extensive Longitudinal Transverse Myelitis Following AstraZeneca COVID-19 Vaccination
Allergic Reactions references
Allergic Reactions to the First COVID-19 Vaccine: A Potential Role of Polyethylene Glycol
Allergic Reactions and Anaphylaxis to LNP-Based COVID-19 Vaccines
Allergic Reactions After COVID-19 Vaccination: Putting the Risk in Perspective
Diffuse Prothrombotic Syndrome After Administration of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccine: Case Report
Concerning the Unexpected Prothrombotic State Following Some Coronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccines (Calcaterra, G., et al.)
Autoantibody Release in Children After Coronavirus mRNA Vaccination: A Risk Factor of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome? (Buchhorn, R., et al.)
Alopecia Areata references
Anaphylaxis references
Reports of Anaphylaxis After Receiving COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines in the U.S.-Dec 14, 2020-Jan 18, 2021
Anaphylaxis Associated with COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines: Approach to Allergy Research
Allergic Reactions and Anaphylaxis to LNP-Based COVID-19 Vaccines
Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) Is a Cause of Anaphylaxis to Pfizer/BioNTech mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine
Anaphylactic Reactions to COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines: A Call for Further Studies
Anaphylaxis Following COVID-19 Vaccine in a Patient With Cholinergic Urticaria
Anaphylaxis Induced by CoronaVac COVID-19 Vaccine: Clinical Features and Results of Revaccination
Sex Differences in the Incidence of Anaphylaxis to LNP-mRNA Vaccines COVID-19
Axillary Adenopathy references
COVID-19 Vaccine-Induced Axillary and Pectoral Lymphadenopathy in PET
Subclinical Axillary Lymphadenopathy Associated With COVID-19 Vaccination on Screening Mammography
Unilateral Axillary Adenopathy in the Setting of COVID-19 Vaccination: Follow-Up
Incidence of Axillary Adenopathy on Breast Imaging After Vaccination with COVID-19
Axillary Lymphadenopathy in Patients With Recent COVID-19 Vaccination: A New Diagnostic Dilemma
COVID-19 Vaccine-Induced Unilateral Axillary Adenopathy: Follow-Up Evaluation in the USA
Bell’s Palsy references
The Association Between COVID-19 Vaccination and Bell’s Palsy
Bell’s Palsy After 24 Hours of mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 Vaccine
Acute Facial Paralysis as a Possible Complication of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination
Bell’s Palsy After COVID-19 Vaccination With High Antibody Response in CSF
Bell’s Palsy After a Single Dose of Vaccine mRNA SARS-CoV-2: Case Report
Adverse Event Reporting and Risk of Bell’s Palsy After COVID-19 Vaccination
Bilateral Facial Nerve Palsy and COVID-19 Vaccination: Causality or Coincidence
Left Bell’s Palsy After the First Dose of mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine: Case Report
Type I Interferons as a Potential Mechanism Linking COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines With Bell’s Palsy
Cardiac Complications references
Transient Cardiac Injury in Adolescents Receiving the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine
A Review of COVID-19 Vaccination and the Reported Cardiac Manifestations
Post-Mortem Investigation of Deaths After Vaccination with COVID-19 Vaccines
COVID-19 Vaccine and Death: Causality Algorithm According to the WHO Eligibility Diagnosis
Myocarditis and Other Cardiovascular Complications of COVID-19 mRNA-based COVID-19 Vaccines
Be Alert to the Risk of Adverse Cardiovascular Events after COVID-19 Vaccination
Myocarditis and Other Cardiovascular Complications of mRNA-based COVID-19 Vaccines
Central Serous Retinopathy references
Cerebral Venous Thrombosis References
Cerebral Venous Thrombosis After BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine
Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis After Vaccination: The United Kingdom Experience
Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Associated with the COVID-19 Vaccine in Germany
The Importance of Recognizing Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Following Anti-COVID-19 Vaccination
Acute Cerebral Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Artery Embolism Associated with the COVID-19 Vaccine
Venous Sinus Thrombosis After Vaccination with ChAdOx1 nCov-19
Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Associated with COVID-19 Vaccine in Germany
Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis Associated with Thrombocytopenia After COVID-19 Vaccination
Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis 2 Weeks After First Dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccine
Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Occurring Shortly After the Second Dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccine
Acute Cerebral Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Artery Embolism Associated with the COVID-19 Vaccine
Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Associated with COVID-19 Vaccine in Germany
Cerebral Venous Thrombosis and Thrombocytopenia After COVID-19 Vaccination
Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis Associated with Vaccine-Induced Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia
Cerebral Venous Thrombosis After the BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine
Lethal Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis After COVID-19 Vaccination
Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis After ChAdOx1 nCov-19 Vaccination with a Misleading First Brain MRI
Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis Associated with Post-Vaccination Thrombocytopenia by COVID-19
Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis 2 Weeks After the First Dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccine
Massive Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Due to Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia
Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Developing After Vaccination, COVID-19: VITT, VATT, TTS and More
Cutaneous Adverse Effects references
Facial Nerve Palsy references
COVID-19 Vaccination Association and Facial Nerve Palsy: A Case-Control Study
Sequential Contralateral Facial Nerve Palsy After First and Second Doses of COVID-19 Vaccine
Peripheral Facial Nerve Palsy After Vaccination with BNT162b2 (COVID-19)
Facial Nerve Palsy After Administration of COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines: Analysis of Self-Report Database
Guillain-Barré Syndrome references
Guillain-Barré Syndrome After AstraZeneca COVID-19 Vaccination: Causal or Casual Association
Guillain-Barré Syndrome Presenting as Facial Diplegia After Vaccination With COVID-19: A Case Report
Guillain-Barré Syndrome After the First Injection of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccine: First Report
SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines Are Not Safe for Those With Guillain-Barre Syndrome Following Vaccination
Guillain Barré Syndrome After Vaccination with mRNA-1273 Against COVID-19
Facial Diplegia: A Rare and Atypical Variant of Guillain-Barré Syndrome and the Ad26.COV2.S Vaccine
Guillain-Barré Syndrome After ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 COVID-19 Vaccination: A Case Series
AstraZeneca COVID-19 Vaccine and Guillain-Barré Syndrome in Tasmania: A Causal Link
COVID-19 Adenovirus Vaccines and Guillain-Barré Syndrome with Facial Palsy
A Case of Guillain-Barré Syndrome After Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine
Guillain-Barré Syndrome Associated with COVID-19 Vaccination
Rate of Recurrent Guillain-Barré Syndrome After COVID-19 BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine
Guillain-Barre Syndrome After COVID-19 Vaccination in an Adolescent
Guillain-Barre Syndrome After ChAdOx1-S / nCoV-19 Vaccination
Guillain-Barre Syndrome After COVID-19 mRNA-1273 Vaccine: Case Report
Guillain-Barre Syndrome Following SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in 19 Patients
A Rare Case of Guillain-Barré Syndrome After COVID-19 Vaccination
Neurological Complications of COVID-19: Guillain-Barre Syndrome After Pfizer COVID-19 Vaccine
COVID-19 Vaccine Causing Guillain-Barre Syndrome, an Uncommon Potential Side Effect
Guillain-Barre Syndrome After the First Dose of COVID-19 Vaccination: Case Report
Guillain-Barre Syndrome After the First Injection of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccine: First Report
A Variant of Guillain-Barré Syndrome After SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination: AMSAN
A Rare Variant of Guillain-Barré Syndrome After Vaccination With Ad26.COV2.S
Guillain-Barré Syndrome in an Australian State Using mRNA and Adenovirus-Vector SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines
Variant Guillain-Barré Syndrome Occurring After SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination
Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis references
Immune-Mediated Disease Outbreaks references
Immune-Mediated Hepatitis references
Autoimmune Hepatitis Triggered by Vaccination Against SARS-CoV-2
Hepatitis C Virus Reactivation After COVID-19 Vaccination: A Case Report
Autoimmune Hepatitis Developing After ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccine (Oxford-AstraZeneca)
Immune-Mediated Hepatitis With the Moderna Vaccine Is No Longer a Coincidence but Confirmed
Intracerebral Haemorrhage references
Intracerebral Haemorrhage Twelve Days After Vaccination With ChAdOx1 nCoV-19
Large Hemorrhagic Stroke After Vaccination Against ChAdOx1 nCoV-19: A Case Report
Major Hemorrhagic Stroke After ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccination: A Case Report
Incidence of Acute Ischemic Stroke After Coronavirus Vaccination in Indonesia: Case Series
Lymphadenopathy references
COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination-Induced Lymphadenopathy Mimics Lymphoma Progression on FDG PET/CT
Lymphadenopathy in COVID-19 Vaccine Recipients: Diagnostic Dilemma in Oncology Patients
Lymphadenopathy After COVID-19 Vaccination: Review of Imaging Findings
A Case of Cervical Lymphadenopathy Following COVID-19 Vaccination
A Case of Cervical Lymphadenopathy Following COVID-19 Vaccination
Evolution of Lymphadenopathy on PET/MRI After COVID-19 Vaccination
Massive Cervical Lymphadenopathy Following Vaccination With COVID-19
Evolution of Lymphadenopathy at PET/MRI After COVID-19 Vaccination
Multiple Sclerosis references
Myocarditis References
Myocarditis after mRNA vaccination against SARS-CoV-2, a case series
Myocarditis after immunization with COVID-19 mRNA vaccines in members of the US military
Acute symptomatic myocarditis in seven adolescents after Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccination
Myocarditis, pericarditis and cardiomyopathy after COVID-19 vaccination
COVID-19 Vaccination Associated with Myocarditis in Adolescents
Acute myocarditis after administration of BNT162b2 vaccine against COVID-19
COVID-19 vaccine-induced myocarditis: a case report with review of the literature
Potential association between COVID-19 vaccine and myocarditis: clinical and CMR findings
Lymphohistocytic myocarditis after vaccination with COVID-19 Ad26.COV2.S viral vector
Myocarditis following vaccination with BNT162b2 in a healthy male
Acute myocarditis after vaccination with SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 mRNA
Acute myocarditis after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in a 24-year-old man
Myocarditis and other cardiovascular complications of COVID-19 mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines
Myocarditis and other cardiovascular complications of COVID-19 mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines
Myocarditis, pericarditis, and cardiomyopathy after COVID-19 vaccination
Association of myocarditis with COVID-19 mRNA vaccine in children
Association of myocarditis with COVID-19 messenger RNA vaccine BNT162b2 in a case series of children
Myocarditis after immunization with COVID-19 mRNA vaccines in members of the U.S. military
Myocarditis occurring after immunization with COVID-19 mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines
Patients with acute myocarditis after vaccination withCOVID-19 mRNA
Symptomatic Acute Myocarditis in 7 Adolescents after Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccination
Cardiac imaging of acute myocarditis after vaccination with COVID-19 mRNA
Case report: acute myocarditis after the second dose of mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine
The new COVID-19 mRNA vaccine platform and myocarditis: clues to the possible underlying mechanism
In-depth evaluation of a case of presumed myocarditis after the second dose of COVID-19 mRNA vaccine
Myocarditis after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination: a vaccine-induced reaction?
Myocarditis and other cardiovascular complications of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines
Case report: acute myocarditis after the second dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 vaccine mRNA-1273
Acute myocardial infarction within 24 hours after COVID-19 vaccination.
Lymphohistocytic myocarditis after vaccination with the COVID-19 viral vector Ad26.COV2.S
Epidemiology of acute myocarditis/pericarditis in Hong Kong adolescents after co-vaccination
Myocarditis and pericarditis after COVID-19 vaccination: inequalities in age and vaccine types.
Myocarditis following BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 mRNA vaccine in Israel.
Myocarditis, pericarditis, and cardiomyopathy following COVID-19 vaccination.
Myocarditis and other cardiovascular complications of COVID-19 mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines.
Possible Association Between COVID-19 Vaccine and Myocarditis: Clinical and CMR Findings.
Severe myocarditis associated with COVID-19 vaccine: zebra or unicorn?.
Acute myocardial infarction and myocarditis after COVID-19 vaccination.
Myocarditis after Covid-19 vaccination in a large healthcare organization.
Association of myocarditis with COVID-19 messenger RNA BNT162b2 vaccine in a case series of children.
STEMI mimicry: focal myocarditis in an adolescent patient after COVID-19 mRNA vaccination.
Patients with acute myocarditis after COVID-19 mRNA vaccination.
Myocarditis associated with COVID-19 vaccination in adolescents.
Myocarditis after COVID-19 vaccination: magnetic resonance imaging study
Acute myocarditis after administration of the second dose of BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine.
Acute myocarditis after administration of BNT162b2 vaccine against COVID-19.
Acute myopericarditis after COVID-19 vaccination in adolescents.
Perimyocarditis in adolescents after Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccination.
Acute myocarditis associated with anti-COVID-19 vaccination.
Myocarditis associated with COVID-19 vaccination: echocardiographic, cardiac CT, and MRI findings.
Acute symptomatic myocarditis in 7 adolescents after Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccination.
Myocarditis and pericarditis in adolescents after First and second doses of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines
COVID 19 vaccine for adolescents. Concern for myocarditis and pericarditis.
Cardiac imaging of acute myocarditis after vaccination with COVID-19 mRNA
Acute myocarditis associated with COVID-19 vaccination: report of a case
Myocarditis following vaccination with COVID-19 messenger RNA: a Japanese case series.
Myocarditis in the setting of a recent COVID-19 vaccination.
Acute myocarditis after a second dose of COVID-19 mRNA vaccine: report of two cases.
Epidemiology of acute myocarditis/pericarditis in Hong Kong adolescents after co-vaccination
Myocarditis and pericarditis after COVID-19 vaccination: inequalities in age and vaccine types
Epidemiology of acute myocarditis/pericarditis in Hong Kong adolescents after co-vaccination
Acute myocarditis after vaccination with COVID-19 mRNA in adults aged 18 years or older
Young male with myocarditis after mRNA-1273 coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) mRNA vaccination
Acute myocarditis after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in a 24-year-old male
Myocarditis Following Immunization with COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines in Members of the U.S. Military
Acute myocarditis after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 mRNA vaccination
Acute myocarditis after Comirnaty vaccination in a healthy male with previous SARS-CoV-2 infection
Acute myocarditis in a young adult two days after vaccination with Pfizer
Acute myocarditis after 2019 coronavirus disease vaccination
Acute myocarditis defined after vaccination with 2019 mRNA of coronavirus disease
Biventricular systolic dysfunction in acute myocarditis after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-1273 vaccination
Myocarditis following vaccination with Covid-19 in a large healthcare organization
Myocarditis after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination, a case series
Acute myocardial infarction and myocarditis after COVID-19 vaccination
Fulminant myocarditis and systemic hyperinflammation temporally associated with BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in two patients - Abbate, A., Gavin, J., Madanchi, N., Kim, C., Shah, P. R., Klein, K., . . . Danielides, S. (2021). Int J Cardiol, 340, 119-121.
Myocarditis following COVID-19 mRNA vaccination - Abu Mouch, S., Roguin, A., Hellou, E., Ishai, A., Shoshan, U., Mahamid, L., . . . Berar Yanay, N. (2021). Vaccine, 39(29), 3790-3793.
Myocarditis following COVID-19 vaccination - Albert, E., Aurigemma, G., Saucedo, J., & Gerson, D. S. (2021). Radiol Case Rep, 16(8), 2142-2145.
Acute Myocardial Infarction and Myocarditis following COVID-19 Vaccination - Aye, Y. N., Mai, A. S., Zhang, A., Lim, O. Z. H., Lin, N., Ng, C. H., . . . Chew, N. W. S. (2021). QJM.
STEMI Mimic: Focal Myocarditis in an Adolescent Patient After mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine - Azir, M., Inman, B., Webb, J., & Tannenbaum, L. (2021). J Emerg Med, 61(6), e129-e132.
Myocarditis With COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines - Bozkurt, B., Kamat, I., & Hotez, P. J. (2021). Circulation, 144(6), 471-484.
COVID 19 Vaccine for Adolescents. Concern about Myocarditis and Pericarditis - Calcaterra, G., Mehta, J. L., de Gregorio, C., Butera, G., Neroni, P., Fanos, V., & Bassareo, P. P. (2021). Pediatr Rep, 13(3), 530-533.
Occurrence of acute infarct-like myocarditis following COVID-19 vaccination: just an accidental co-incidence or rather vaccination-associated autoimmune myocarditis? - Chamling, B., Vehof, V., Drakos, S., Weil, M., Stalling, P., Vahlhaus, C., . . . Yilmaz, A. (2021). Clin Res Cardiol, 110(11), 1850-1854.
Cardiac MRI Findings of Myocarditis After COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination in Adolescents - Chelala, L., Jeudy, J., Hossain, R., Rosenthal, G., Pietris, N., & White, C. (2021). AJR Am J Roentgenol.
Myocarditis-induced Sudden Death after BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination in Korea: Case Report Focusing on Histopathological Findings - Choi, S., Lee, S., Seo, J. W., Kim, M. J., Jeon, Y. H., Park, J. H., . . . Yeo, N. S. (2021). J Korean Med Sci, 36(40), e286.
Epidemiology of Acute Myocarditis/Pericarditis in Hong Kong Adolescents Following Comirnaty Vaccination - Chua, G. T., Kwan, M. Y. W., Chui, C. S. L., Smith, R. D., Cheung, E. C., Tian, T., . . . Ip, P. (2021). Clin Infect Dis.
Should T2 mapping be used in cases of recurrent myocarditis to differentiate between acute inflammation and chronic scar? - Clarke, R., & Ioannou, A. (2021). J Pediatr.
Myocarditis and Pericarditis Following mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination: What Do We Know So Far? - Das, B. B., Moskowitz, W. B., Taylor, M. B., & Palmer, A. (2021). Children (Basel), 8(7).
A Series of Patients With Myocarditis Following SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination With mRNA-1279 and BNT162b2 - Dickey, J. B., Albert, E., Badr, M., Laraja, K. M., Sena, L. M., Gerson, D. S., . . . Aurigemma, G. P. (2021). JACC Cardiovasc Imaging, 14(9), 1862-1863.
Biopsy-proven lymphocytic myocarditis following thefirst mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in a 40-year-old male: case report - Ehrlich, P., Klingel, K., Ohlmann-Knafo, S., Huttinger, S., Sood, N., Pickuth, D., & Kindermann, M. (2021). Clin Res Cardiol, 110(11), 1855-1859.
Acute myocarditis in a young adult two days after Pfizer vaccination - Facetti, S., Giraldi, M., Vecchi, A. L., Rogiani, S., & Nassiacos, D. (2021). G Ital Cardiol (Rome), 22(11), 891-893.
Myocarditis and Pericarditis in Adolescents after First and Second doses of mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines - Foltran, D., Delmas, C., Flumian, C., De Paoli, P., Salvo, F., Gautier, S., . . . Montastruc, F. (2021). Eur Heart J Qual Care Clin Outcomes.
Use of mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine After Reports of Myocarditis Among Vaccine Recipients: Update from the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices – United States, June 2021 - Gargano, J. W., Wallace, M., Hadler, S. C., Langley, G., Su, J. R., Oster, M. E., . . . Oliver, S. E. (2021). MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, 70(27), 977-982.
A Late Presentation of COVID-19 Vaccine-Induced Myocarditis - Gautam, N., Saluja, P., Fudim, M., Jambhekar, K., Pandey, T., & Al’Aref, S. (2021). Cureus, 13(9), e17890.
Myocarditis after vaccination against COVID-19 - Gellad, W. F. (2021). BMJ, 375, n3090.
Myocarditis with the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines - In brief: Myocarditis with the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines. (2021). Med Lett Drugs Ther, 63(1629), e9.
Myocarditis should be considered in those with a troponin rise and unobstructed coronary arteries following Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccination - Ioannou, A. (2021a). QJM. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcab231.
T2 mapping should be utilized in cases of suspected myocarditis to confirm an acute inflammatory process - Ioannou, A. (2021b). QJM. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcab326.
Myocarditis Following COVID-19 Vaccination - Isaak, A., Feisst, A., & Luetkens, J. A. (2021). Radiology, 301(1), E378-E379. doi:10.1148/radiol.2021211766.
Myocarditis and pericarditis in association with COVID-19 mRNA-vaccination: cases from a regional pharmacovigilance centre - Istampoulouoglou, I., Dimitriou, G., Spani, S., Christ, A., Zimmermanns, B., Koechlin, S., . . . Leuppi-Taegtmeyer, A. B. (2021). Glob Cardiol Sci Pract, 2021(3), e202118. doi:10.21542/gcsp.2021.18.
COVID-19 Vaccination-Associated Myocarditis in Adolescents - Jain, S. S., Steele, J. M., Fonseca, B., Huang, S., Shah, S., Maskatia, S. A., . . . Grosse-Wortmann, L. (2021). Pediatrics, 148(5). doi:10.1542/peds.2021-053427.
Young Male With Myocarditis Following mRNA-1273 Vaccination Against Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19) - Kaneta, K., Yokoi, K., Jojima, K., Kotooka, N., & Node, K. (2021). Circ J. doi:10.1253/circj.CJ-21-0818.
Myocarditis following COVID-19 vaccination - Kaul, R., Sreenivasan, J., Goel, A., Malik, A., Bandyopadhyay, D., Jin, C., . . . Panza, J. A. (2021). Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc, 36, 100872. doi:10.1016/j.ijcha.2021.100872.
Patients With Acute Myocarditis Following mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination - Kim, H. W., Jenista, E. R., Wendell, D. C., Azevedo, C. F., Campbell, M. J., Darty, S. N., . . . Kim, R. J. (2021). JAMA Cardiol, 6(10), 1196-1201. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2021.2828.
Cardiac Imaging of Acute Myocarditis Following COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination - Kim, I. C., Kim, H., Lee, H. J., Kim, J. Y., & Kim, J. Y. (2021). J Korean Med Sci, 36(32), e229. doi:10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e229.
Myocarditis following mRNA vaccination against SARS-CoV-2, a case series - King, W. W., Petersen, M. R., Matar, R. M., Budweg, J. B., Cuervo Pardo, L., & Petersen, J. W. (2021). Am Heart J Plus, 8, 100042. doi:10.1016/j.ahjo.2021.100042.
mRNA COVID vaccine and myocarditis in adolescents - Kwan, M. Y. W., Chua, G. T., Chow, C. B., Tsao, S. S. L., To, K. K. W., Yuen, K. Y., . . . Ip, P. (2021). Hong Kong Med J, 27(5), 326-327. doi:10.12809/hkmj215120.
Reply to “Letter to the editor: Myocarditis should be considered in those with a troponin rise and unobstructed coronary arteries following Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccination” - Lee, E., Chew, N. W. S., Ng, P., & Yeo, T. J. (2021). QJM. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcab232.
Myocarditis following COVID-19 vaccination – A case series - Levin, D., Shimon, G., Fadlon-Derai, M., Gershovitz, L., Shovali, A., Sebbag, A., . . . Gordon, B. (2021). Vaccine, 39(42), 6195-6200. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.09.004.
Myocarditis and Pericarditis following COVID-19 Vaccination: Inequalities in Age and Vaccine Types - Li, M., Yuan, J., Lv, G., Brown, J., Jiang, X., & Lu, Z. K. (2021). J Pers Med, 11(11). doi:10.3390/jpm11111106.
Case Report: Acute Fulminant Myocarditis and Cardiogenic Shock After Messenger RNA Coronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccination Requiring Extracorporeal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation - Lim, Y., Kim, M. C., Kim, K. H., Jeong, I. S., Cho, Y. S., Choi, Y. D., & Lee, J. E. (2021). Front Cardiovasc Med, 8, 758996. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2021.758996.
Myocarditis and Pericarditis After COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination: Practical Considerations for Care Providers - Luk, A., Clarke, B., Dahdah, N., Ducharme, A., Krahn, A., McCrindle, B., . . . McDonald, M. (2021). Can J Cardiol, 37(10), 1629-1634. doi:10.1016/j.cjca.2021.08.001.
Myocarditis after BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine against Covid-19 in Israel - Mevorach, D., Anis, E., Cedar, N., Bromberg, M., Haas, E. J., Nadir, E., . . . Alroy-Preis, S. (2021). N Engl J Med, 385(23), 2140-2149. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2109730.
Recurrence of Acute Myocarditis Temporally Associated with Receipt of the mRNA Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Vaccine in a Male Adolescent - Minocha, P. K., Better, D., Singh, R. K., & Hoque, T. (2021). J Pediatr, 238, 321-323. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2021.06.035.
Myocarditis Following Immunization With mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines in Members of the US Military - Montgomery, J., Ryan, M., Engler, R., Hoffman, D., McClenathan, B., Collins, L., . . . Cooper, L. T., Jr. (2021). JAMA Cardiol, 6(10), 1202-1206. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2021.2833.
Myocarditis Following a COVID-19 Messenger RNA Vaccination: A Japanese Case Series - Murakami, Y., Shinohara, M., Oka, Y., Wada, R., Noike, R., Ohara, H., . . . Ikeda, T. (2021). Intern Med. doi:10.2169/internalmedicine.8731-21.
Acute Myocarditis Associated with COVID-19 Vaccination: A Case Report - Nagasaka, T., Koitabashi, N., Ishibashi, Y., Aihara, K., Takama, N., Ohyama, Y., . . . Kaneko, Y. (2021). J Cardiol Cases. doi:10.1016/j.jccase.2021.11.006.
Epidemiology and Clinical Features of Myocarditis/Pericarditis before the Introduction of mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine in Korean Children: a Multicenter Study - Park, H., Yun, K. W., Kim, K. R., Song, S. H., Ahn, B., Kim, D. R., . . . Kim, Y. J. (2021). J Korean Med Sci, 36(32), e232. doi:10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e232.
Self-limited myocarditis presenting with chest pain and ST segment elevation in adolescents after vaccination with the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine - Park, J., Brekke, D. R., & Bratincsak, A. (2021). Cardiol Young, 1-doi:10.1017/S1047951121002547.
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance findings in young adult patients with acute myocarditis following mRNA COVID-19 vaccination: a case - Patel, Y. R., Louis, D. W., Atalay, M., Agarwal, S., & Shah, N. R. (2021). J Cardiovasc Magn Reson, 23(1), 101. doi:10.1186/s12968-021-00795-1.
Risks of myocarditis, pericarditis, and cardiac arrhythmias associated with COVID-19 vaccination or SARS-CoV-2 infection - Patone, M., Mei, X. W., Handunnetthi, L., Dixon, S., Zaccardi, F., Shankar-Hari, M., . . . Hippisley-Cox, J. (2021). Nat Med. doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01630-1.
Acute myocarditis following Comirnaty vaccination in a healthy man with previous SARS-CoV-2 infection - Patrignani, A., Schicchi, N., Calcagnoli, F., Falchetti, E., Ciampani, N., Argalia, G., & Mariani, A. (2021). Radiol Case Rep, 16(11), 3321-3325. doi:10.1016/j.radcr.2021.07.082.
Myocarditis Following COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine: A Case Series and Incidence Rate Determination - Perez, Y., Levy, E. R., Joshi, A. Y., Virk, A., Rodriguez-Porcel, M., Johnson, M., . . . Swift, M. D. (2021). Clin Infect Dis. doi:10.1093/cid/ciab926.
Myocarditis following COVID-19 vaccination: magnetic resonance imaging study - Shiyovich, A., Witberg, G., Aviv, Y., Eisen, A., Orvin, K., Wiessman, M., . . . Hamdan, A. (2021). Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. doi:10.1093/ehjci/jeab230.
Acute Myocarditis Following COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination in Adults Aged 18 Years or Older - Simone, A., Herald, J., Chen, A., Gulati, N., Shen, A. Y., Lewin, B., & Lee, M. S. (2021). JAMA Intern Med, 181(12), 1668-1670. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.5511.
Risk of Myocarditis from COVID-19 Infection in People Under Age 20: A Population-Based Analysis - Singer, M. E., Taub, I. B., & Kaelber, D. C. (2021). medRxiv. doi:10.1101/2021.07.23.21260998.
Myocarditis Associated with mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination - Starekova, J., Bluemke, D. A., Bradham, W. S., Grist, T. M., Schiebler, M. L., & Reeder, S. B. (2021). Radiology, 301(2), E409-E411. doi:10.1148/radiol.2021211430.
Temporal association between the COVID-19 Ad26.COV2.S vaccine and acute myocarditis: A case report and literature review - Sulemankhil, I., Abdelrahman, M., & Negi, S. I. (2021). Cardiovasc Revasc Med. doi:10.1016/j.carrev.2021.08.012.
Case report: acute myocarditis following the second dose of mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine - Tailor, P. D., Feighery, A. M., El-Sabawi, B., & Prasad, A. (2021). Eur Heart J Case Rep, 5(8), ytab319. doi:10.1093/ehjcr/ytab319.
Eosinophilic Myocarditis Following Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Vaccination - Takeda, M., Ishio, N., Shoji, T., Mori, N., Matsumoto, M., & Shikama, N. (2021). Circ J. doi:10.1253/circj.CJ-21-935.
Clinically Suspected Myocarditis Temporally Related to COVID-19 Vaccination in Adolescents and Young Adults - Truong, D. T., Dionne, A., Muniz, J. C., McHugh, K. E., Portman, M. A., Lambert, L. M., . . . Newburger, J. W. (2021). Circulation. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.056583.
Myocarditis and Other Cardiovascular Complications of the mRNA-Based COVID-19 Vaccines - Vidula, M. K., Ambrose, M., Glassberg, H., Chokshi, N., Chen, T., Ferrari, V. A., & Han, Y. (2021). Cureus, 13(6), e15576. doi:10.7759/cureus.15576.
Myocarditis Following mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine - Visclosky, T., Theyyunni, N., Klekowski, N., & Bradin, S. (2021). Pediatr Emerg Care, 37(11), 583-584. doi:10.1097/PEC.0000000000002557.
Myocarditis after BNT162b2 vaccination in a healthy male - Watkins, K., Gri몭 n, G., Septaric, K., & Simon, E. L. (2021). Am J Emerg Med, 50, 815 e811-815 e812. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2021.06.051.
Myocarditis after Covid-19 Vaccination in a Large Health Care Organization - Witberg, G., Barda, N., Hoss, S., Richter, I., Wiessman, M., Aviv, Y., . . . Kornowski, R. (2021). N Engl J Med, 385(23), 2132-2139. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2110737.
Myocarditis with the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines (2021). Med Lett Drugs Ther, 63(1629), e9. Retrieved from PubMed
Myocarditis should be considered in those with a troponin rise and unobstructed coronary arteries following Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccination. QJM. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcab231. Author: Ioannou, A.
Myocarditis Following COVID-19 Vaccination. Radiology, 301(1), E378-E379. doi:10.1148/radiol.2021211766. Authors: Isaak, A., Feisst, A., & Luetkens, J. A.
Myocarditis and pericarditis in association with COVID-19 mRNA-vaccination: cases from a regional pharmacovigilance centre. Glob Cardiol Sci Pract, 2021(3), e202118. doi:10.21542/gcsp.2021.18. Authors: Istampoulouoglou, I., Dimitriou, G., Spani, S., Christ, A., Zimmermanns, B., Koechlin, S., . . . Leuppi-Taegtmeyer, A. B.
COVID-19 Vaccination-Associated Myocarditis in Adolescents. Pediatrics, 148(5). doi:10.1542/peds.2021-053427. Authors: Jain, S. S., Steele, J. M., Fonseca, B., Huang, S., Shah, S., Maskatia, S. A., . . . Grosse-Wortmann, L.
Young Male With Myocarditis Following mRNA-1273 Vaccination Against Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19). Circ J. doi:10.1253/circj.CJ-21-0818. Authors: Kaneta, K., Yokoi, K., Jojima, K., Kotooka, N., & Node, K.
Myocarditis following COVID-19 vaccination. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc, 36, 100872. doi:10.1016/j.ijcha.2021.100872. Authors: Kaul, R., Sreenivasan, J., Goel, A., Malik, A., Bandyopadhyay, D., Jin, C., . . . Panza, J. A.
Patients With Acute Myocarditis Following mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination. JAMA Cardiol, 6(10), 1196-1201. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2021.2828. Authors: Kim, H. W., Jenista, E. R., Wendell, D. C., Azevedo, C. F., Campbell, M. J., Darty, S. N., . . . Kim, R. J.
Cardiac Imaging of Acute Myocarditis Following COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination. J Korean Med Sci, 36(32), e229.doi:10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e229. Authors: Kim, I. C., Kim, H., Lee, H. J., Kim, J. Y., & Kim, J. Y.
Myocarditis following mRNA vaccination against SARS-CoV-2, a case series. Am Heart J Plus, 8, 100042. doi:10.1016/j.ahjo.2021.100042. Authors: King, W. W., Petersen, M. R., Matar, R. M., Budweg, J. B., Cuervo Pardo, L., & Petersen, J. W.
mRNA COVID vaccine and myocarditis in adolescents. Hong Kong Med J, 27(5), 326-327. doi:10.12809/hkmj215120. Authors: Kwan, M. Y. W., Chua, G. T., Chow, C. B., Tsao, S. S. L., To, K. K. W., Yuen, K. Y., . . . Ip, P.
Reply to “Letter to the editor: Myocarditis should be considered in those with a troponin rise and unobstructed coronary arteries following PfizerBioNTech COVID-19 vaccination”. QJM.doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcab232. Authors: Lee, E., Chew, N. W. S., Ng, P., & Yeo, T. J.
Myocarditis following COVID-19 vaccination – A case series. Vaccine, 39(42), 6195-6200.doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.09.004. Authors: Levin, D., Shimon, G., Fadlon-Derai, M., Gershovitz, L., Shovali, A., Sebbag, A., . . . Gordon, B.
Myocarditis and Pericarditis following COVID-19 Vaccination: Inequalities in Age and Vaccine Types. J Pers Med, 11(11). doi:10.3390/jpm11111106. Authors: Li, M., Yuan, J., Lv, G., Brown, J., Jiang, X., & Lu, Z. K.
Acute Fulminant Myocarditis and Cardiogenic Shock After Messenger RNA Coronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccination Requiring Extracorporeal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation. Front Cardiovasc Med, 8, 758996. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2021.758996. Authors: Lim, Y., Kim, M. C., Kim, K. H., Jeong, I. S., Cho, Y. S., Choi, Y. D., & Lee, J. E.
Myocarditis and Pericarditis After COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination: Practical Considerations for Care Providers. Can J Cardiol, 37(10), 1629-1634.doi:10.1016/j.cjca.2021.08.001. Authors: Luk, A., Clarke, B., Dahdah, N., Ducharme, A., Krahn, A., McCrindle, B., . . . McDonald, M.
Myocarditis after BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine against Covid-19 in Israel. N Engl J Med, 385(23), 2140-2149. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2109730. Authors: Mevorach, D., Anis, E., Cedar, N., Bromberg, M., Haas, E. J., Nadir, E., . . . Alroy-Preis, S.
Recurrence of Acute Myocarditis Temporally Associated with Receipt of the mRNA Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Vaccine in a Male Adolescent. J Pediatr, 238, 321-323.doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2021.06.035. Authors: Minocha, P. K., Better, D., Singh, R. K., & Hoque, T.
Myocarditis Following Immunization With mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines in Members of the US Military. JAMA Cardiol, 6(10), 1202-1206.doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2021.2833. Authors: Montgomery, J., Ryan, M., Engler, R., Hoffman, D., McClenathan, B., Collins, L., . . . Cooper, L. T., Jr.
Myocarditis Following a COVID-19 Messenger RNA Vaccination: A Japanese Case Series. Intern Med. doi:10.2169/internalmedicine.8731-21. Authors: Murakami, Y., Shinohara, M., Oka, Y., Wada, R., Noike, R., Ohara, H., . . . Ikeda, T.
Acute Myocarditis Associated with COVID-19 Vaccination: A Case Report. Authors: Nagasaka, T., Koitabashi, N., Ishibashi, Y., Aihara, K., Takama, N., Ohyama, Y., . . . Kaneko, Y. Published in J Cardiol Cases. doi:10.1016/j.jccase.2021.11.006.
Premature Myocardial Infarction or Side Effect of COVID-19 Vaccine.
Features of Inflammatory Heart Reactions Following mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination at a Global Level. Authors: Chouchana, L., Blet, A., Al-Khalaf, M., Kaffl, T. S., Nair, G., Robblee, J., . . . Liu, P. P. Published in Clin Pharmacol Ther. doi:10.1002/cpt.2499.
Lymphohistocytic Myocarditis after Ad26.COV2.S Viral Vector COVID-19 Vaccination.
Myopericarditis
Myopericarditis after Pfizer mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination in Adolescents
Myopericarditis after Vaccination with COVID-19 mRNA in Adolescents 12 to 18 Years of Age
Important Information on Myopericarditis after Vaccination with Pfizer COVID-19 mRNA in Adolescents
Acute Myocarditis after Administration of BNT162b2 Vaccine against COVID-19
COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination and Development of CMR-Confirmed Myopericarditis
Myopericarditis in a Previously Healthy Adolescent Male after COVID-19 Vaccination: Case Report
Myopericarditis after Pfizer Messenger Ribonucleic Acid Coronavirus Disease Vaccine in Adolescents
Population-based Incidence of Myopericarditis After COVID-19 Vaccination in Danish Adolescents
mRNA Coronavirus-19 Vaccine-Associated Myopericarditis in Adolescents: A Survey Study
Important Insights into Myopericarditis after the Pfizer mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination in Adolescents
Recurrence of Myopericarditis Following mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination in a Male Adolescent
Influenza Vaccination and Myo-Pericarditis in Patients Receiving Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
Myopericarditis in a Previously Healthy Adolescent Male After COVID-19 Vaccination: Case Report
Pericarditis references
Myocarditis, Pericarditis, and Cardiomyopathy After COVID-19 Vaccination
Pericarditis After Administration of BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine
Myocarditis, Pericarditis, and Cardiomyopathy After COVID-19 Vaccination
Acute Myocarditis After the Second Dose of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine: Serendipity or Causal Relationship
Pericarditis After Administration of COVID-19 mRNA BNT162b2 Vaccine
Unusual Presentation of Acute Pericarditis After Vaccination Against SARS-COV-2 mRNA-1237 Modern
Acute Pericarditis and Cardiac Tamponade After Vaccination with Covid-19
Pericarditis After Administration of the BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine COVID-19
Case Report: Symptomatic Pericarditis Post COVID-19 Vaccination
Perimyocarditis references
Prion Disease references
Psoriasis references
Purpura Annularis Telangiectodes references
Rhabdomyolysis references
Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy references
Myocarditis, Pericarditis, and Cardiomyopathy After COVID-19 Vaccination
Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy After Vaccination with mRNA COVID-19
Takotsubo (Stress) Cardiomyopathy After Vaccination with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19
Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy After Coronavirus 2019 Vaccination in a Patient on Maintenance Hemodialysis
Thrombocytopenia References
Thrombosis with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Associated with COVID-19 Vaccines.
Thrombosis with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Associated with COVID-19 Viral Vector Vaccines.
Thrombotic Immune Thrombocytopenia Induced by SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine.
Thrombosis and Thrombocytopenia After Vaccination with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19.
Post-Mortem Findings in Vaccine-Induced Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia (COVID-19).
Vaccine-Induced Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia: The Dark Chapter of a Success Story.
Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura After Vaccination with COVID-19 Vaccine (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19).
Thrombocytopenia Following Pfizer and Moderna SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination
Severe and Refractory Immune Thrombocytopenia Occurring After SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination
Purpuric Rash and Thrombocytopenia After mRNA-1273 (Moderna) COVID-19 Vaccine
Thrombosis with Thrombocytopenia After Messenger RNA Vaccine-1273
Exacerbation of Immune Thrombocytopenia After COVID-19 Vaccination
PF4 Immunoassays in Vaccine-Induced Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia
Antibody Epitopes in Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia
Thrombosis with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Associated with COVID-19 Vaccines
Immune Thrombocytopenia Associated with Pfizer-BioNTech’s COVID-19 BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine
Laboratory Testing for Suspicion of COVID-19 Vaccine-Induced Thrombotic (Immune) Thrombocytopenia
Immune Thrombocytopenia in a 22-Year-Old Post COVID-19 Vaccine
Secondary Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP) Associated with ChAdOx1 COVID-19 Vaccine: Case Report
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia After Vaccination with COVID-19: In Search of the Underlying Mechanism
Thrombosis and SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines: Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia
Immune Complexes, Innate Immunity and NETosis in ChAdOx1 Vaccine-Induced Thrombocytopenia
Immune-Mediated Thrombocytopenic Purpura After Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine in an Elderly Woman
Immune-Mediated Thrombocytopenia Associated with Ad26.COV2.S Vaccine (Janssen; Johnson & Johnson)
Immune Thrombocytopenia After Vaccination During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Thrombocytopenia in an Adolescent with Sickle Cell Anemia After COVID-19 Vaccination
ChAdOx1 Interacts with CAR and PF4 with Implications for Thrombosis with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome
VITT (Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia) After Vaccination with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19
Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis After Vaccination: The UK Experience
Venous Thromboembolism and Mild Thrombocytopenia After Vaccination with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19
COVID-19 Vaccine-Induced Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia: A Case Series
Case Report of Immune Thrombocytopenia After Vaccination with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19
Thrombocytopenia in an Adolescent with Sickle Cell Anemia After COVID-19 Vaccination
Venous Thromboembolism and Mild Thrombocytopenia After ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccination
Relapse of Immune Thrombocytopenia After COVID-19 Vaccination
Images of Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia Induced by Oxford/AstraZeneca® COVID-19 Vaccine
Complicated Case Report of Long-Term Vaccine-Induced Thrombotic Immune Thrombocytopenia A
Severe, Refractory Immune Thrombocytopenia Occurring After SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine
Thrombocytopenia Following Pfizer and Moderna SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination
Relapse of Immune Thrombocytopenia After COVID-19 Vaccination in Young Male Patient
Thrombosis references
Three Cases of Acute Venous Thromboembolism in Women After Vaccination Against COVID-19.
Acute Thrombosis of the Coronary Tree After Vaccination Against COVID-19.
Portal Vein Thrombosis Associated with ChAdOx1 nCov-19 Vaccine.
Thrombosis With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Associated With COVID-19 Vaccines.
Thrombosis With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Associated With COVID-19 Viral Vector Vaccines.
Roots of Autoimmunity of Thrombotic Events After COVID-19 Vaccination.
Thrombotic Immune Thrombocytopenia Induced by SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine.
Thrombosis and Thrombocytopenia After Vaccination with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19.
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia After Vaccination with ChAdOx1 nCov-19.
Post-Mortem Findings in Vaccine-Induced Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia (COVID-19).
Comparison of Vaccine-Induced Thrombotic Episodes Between ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and Ad26.COV.2.S Vaccines.
Prothrombotic Immune Thrombocytopenia After COVID-19 Vaccination.
Vaccine-Induced Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia: The Dark Chapter of a Success Story.
Thrombosis After COVID-19 Vaccination: Possible Link to ACE Pathways.
Thrombosis With Thrombocytopenia After Messenger RNA Vaccine-1273.
PF4 Immunoassays in Vaccine-Induced Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia.
Antibody Epitopes in Vaccine-Induced Immune Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia.
Thrombosis With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Associated With COVID-19 Vaccines.
Laboratory Testing for Suspicion of COVID-19 Vaccine-Induced Thrombotic (Immune) Thrombocytopenia.
Comparison of Vaccine-Induced Thrombotic Events Between ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and Ad26.COV.2.S Vaccines.
Thrombosis With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome After COVID-19 Immunization.
Thrombosis With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Associated With COVID-19 Viral Vector Vaccines.
Vaccine-Induced Thrombosis and Thrombocytopenia With Bilateral Adrenal Hemorrhage.
Palmar Digital Vein Thrombosis After Oxford-AstraZeneca COVID-19 Vaccination.
Thrombosis With Thrombocytopenia After Messenger Vaccine RNA-1273.
Coronavirus (COVID-19) Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia (VITT).
Immunoglobulin Adjuvant for Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia.
Immune Thrombocytopenia Associated With the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine BNT162b2.
Secondary Immune Thrombocytopenia Putatively Attributable to COVID-19 Vaccination.
Immune Thrombocytopenia Following Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine.
Newly Diagnosed Idiopathic Thrombocytopenia After COVID-19 Vaccine Administration.
Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura and the Modern COVID-19 Vaccine.
Thrombocytopenia After Pfizer and Moderna SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination.
Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura and Acute Liver Injury After COVID-19 Vaccination.
Carotid Artery Immune Thrombosis Induced by Adenovirus-Vectored COVID-19 Vaccine: Case Report.
Autoimmunity Roots of Thrombotic Events After Vaccination With COVID-19.
Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis After Vaccination: The UK Experience.
Rare Case of COVID-19 Vaccine-Associated Intracranial Hemorrhage With Venous Sinus Thrombosis.
Clinical Features of Vaccine-Induced Thrombocytopenia and Immune Thrombosis.
Possible Triggers of Thrombocytopenia and/or Hemorrhage by BNT162b2 Vaccine, Pfizer-BioNTech.
Case Series of Vaccine-Induced Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia in a London Teaching Hospital.
Genital Necrosis With Cutaneous Thrombosis Following Vaccination With COVID-19 mRNA.
Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis After mRNA-Based COVID-19 Vaccination.
Thrombosis with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Associated with COVID-19 Vaccines.
Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis After COVID-19 Vaccination: Neurologic and Radiologic Management.
Case Report: Cerebral Sinus Vein Thrombosis in Two Patients with AstraZeneca SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine.
Thrombosis After COVID-19 Vaccination: Possible Link to ACE Pathways.
Major Artery Thrombosis and Vaccination Against ChAdOx1 nCov-19.
An Unusual Presentation of Acute Deep Vein Thrombosis After Modern COVID-19 Vaccine: Case Report.
Thrombosis Formation After COVID-19 Vaccination Immunologic Aspects: Review Article.
Fatal Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis After COVID-19 Vaccination.
Autoimmune Roots of Thrombotic Events After COVID-19 Vaccination.
New Portal Vein Thrombosis in Cirrhosis: Is Thrombophilia Exacerbated by Vaccine or COVID-19.
Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis After Vaccination With COVID-19 mRNA of BNT162b2.
Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis Following Vaccination With Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 (BNT162b2).
Thromboembolic Events in Younger Females Exposed to Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna COVID-19 Vaccines.
Thrombosis After Adenovirus-Vectored COVID-19 Vaccination: A Concern for Underlying Disease.
Deep Venous Thrombosis After Vaccination With Ad26.COV2.S in Adult Males.
Post-mortem Findings in Vaccine-Induced Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia.
Anaphylactoid Reaction and Coronary Thrombosis Related to COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine.
Occurrence of Splenic Infarction Due to Arterial Thrombosis After Vaccination With COVID-19.
Deep Venous Thrombosis More Than Two Weeks After COVID-19 Vaccination.
Information on ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccine-Induced Immune-Mediated Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia.
Three Cases of Acute Venous Thromboembolism in Women After Coronavirus 2019 Vaccination.
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura references
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura after Vaccination with Ad26.COV2-S
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: A New Threat after COVID BNT162b2 Vaccine
Severe Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura after SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine
Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura Associated with COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine Pfizer-BioNTech BNT16B2b2
Vasculitis References
ANCA-Associated Vasculitis After Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine
IgA Vasculitis in Adult Patient After Vaccination with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19
A Case of Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis After Vaccination with a SARS-CoV2 Vaccine: Case Report
Induction of Cutaneous Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis After ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccine
Intracerebral Hemorrhage Due to Vasculitis Following COVID-19 Vaccination: Case Report
ANCA-Associated Vasculitis After Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine
New-Onset Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis After COVID-19 Vaccine
Outbreak of Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis After COVID-19 Vaccine
Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis After Exposure to COVID-19 Vaccine
Vasculitis and Bursitis in [18F] FDG-PET/CT After COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine: Post Hoc Ergo Propter Hoc?
Cutaneous Lymphocytic Vasculitis After Administration of COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine
Cutaneous Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis Induced by Sinovac COVID-19 Vaccine
Reactivation of IgA Vasculitis After Vaccination with COVID-19
Varicella-Zoster Virus-Related Small-Vessel Vasculitis After Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccination
Imaging in Vascular Medicine: Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis After COVID-19 Vaccine Booster
Possible Case of COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine-Induced Small-Vessel Vasculitis
First Description of Immune Complex Vasculitis After COVID-19 Vaccination with BNT162b2: Case Report
Nephrotic Syndrome and Vasculitis After SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine: True Association or Circumstantial
Occurrence of De Novo Cutaneous Vasculitis After Vaccination Against Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19)
Asymmetric Cutaneous Vasculitis After COVID-19 Vaccination with Unusual Preponderance of Eosinophils
Granulomatous Vasculitis After AstraZeneca Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine
A Case of Generalized Sweet’s Syndrome with Vasculitis Triggered by Recent Vaccination with COVID-19
Small-Vessel Vasculitis Following Oxford-AstraZeneca Vaccination Against SARS-CoV-19
Cutaneous Vasculitis After Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Vaccine
Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis After Coronavirus Disease Vaccination 2019
Outbreaks of Mixed Cryoglobulinemia Vasculitis After Vaccination Against SARS-CoV-2
Cutaneous Small-Vessel Vasculitis After Vaccination with a Single Dose of Janssen Ad26.COV2.S
Case of Immunoglobulin A Vasculitis After Vaccination Against Coronavirus Disease 2019
Relapse of Microscopic Polyangiitis After COVID-19 Vaccination: Case Report